Warehouse heating
Warehouse – a room for storing material assets and working with them. Climatic conditions in the warehouse must meet sanitary, hygienic, and technological standards; ensure the safety of contents and the comfort of employees. This requires heating the warehouse.
Standards for proper heating of a warehouse
Proper heating of the warehouse is based on building codes SP 31-110-2003, SNiP 31-04-2001, SNiP 2.04.05-91, SNiP 2.11.01-85 “Warehouse buildings”. They say:
- heating surfaces must be protected from possible contact with combustible substances, provided that heating can be arranged in the fire hazardous area using
- exclusively electric heaters;
- electricity receivers of the heating system must be of the same category as the receivers related to the engineering and technological equipment of the warehouse;
- when using air heaters in a warehouse, it is necessary to provide protection against overheating;
- it is impossible to use heating devices that provide a direct transition of electrical energy into thermal energy in warehouses where combustible materials are stored;
- when installing a water and steam heating system, the maximum allowable steam temperature in warehouses of categories A, B, and C, if dust and aerosols are not emitted, is 130 ° C (water – 150 ° C);
- when installing a water and steam heating system, the maximum allowable temperature in warehouses of categories A, and B during the release of dust and aerosols, is 110 ° C, category C – 130 ° C;
- water and steam heating cannot be installed if there are substances in the warehouse that can become combustible when interacting with water or steam.
Warehouse heating: types of systems

Traditionally, central heating is used to heat warehouses. Thermal equipment is a single device that is installed indoors. Depending on the type of heat carrier, the warehouse heating system can be:
- steam (operates on dry saturated steam);
- air (works on heated air);
- water (runs on water or antifreeze).
These warehouse heating systems can be combined with each other.
Steam and water systems, compared with air, have a number of disadvantages:
- high heat losses in steam pipelines;
- the temperature of the heat carrier cannot be lower than 100 °C;
- metal elements of the system are subject to corrosion;
- work noisily.
If there is no heating system in the warehouse, it is forced to be introduced. An example is the heating of a cold warehouse. It is necessary if the stored material values do not tolerate low temperatures without losing their qualities. If the goods are not refrozen under such conditions, then there is no need to heat the cold store (unlike utility rooms for workers).
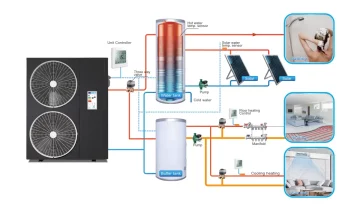
When the question of saving heating costs arises, they resort to autonomous heating of warehouses. It does not depend on gas communications, it can be organized independently of electricity.
Autonomous heating of warehouses works with the help of:
- solid fuel boiler;
- diesel fuel;
- liquefied gas;
- heat pump;
- solar energy.
Solar energy for warehouse heating
The use of alternative energy sources for heating warehouses is a non-standard approach. It has a number of advantages:
- cost savings – unlike gas and electricity, you do not need to pay for solar energy;
- accessibility – the sun is everywhere, but engineering communications are not;
- autonomy and security.
There is no central heating in the UK, Japan, Germany, France, and Finland, and solar energy has become an excellent alternative for it. It is used not only for heating residential and office premises but also for heating a warehouse.
Read more about the use of an air solar collector for heating warehouses in the section “Application”.