Solar panels on the balcony – what’s the effect
Solar power stations on balconies are becoming increasingly popular. But do such systems pay off? And what should you pay attention to?
The transition to alternative energy sources in Germany is at its peak. Special interest in the last year has been generated by so-called “plug-in solar power stations.” According to the Federal Network Agency, in the first quarter of this year, the number of registered small systems increased sevenfold compared to the same period last year. By 2030, the number of mini solar power stations could reach 12 million.
In addition to solar panels on the roof, some German municipal companies have allowed them to be installed on balconies. In other European countries such as Poland, France, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, Austria, Switzerland, and Hungary, there has also been a noticeable increase in interest in energy-saving technologies, which, in addition to their environmental friendliness, are relatively easy to maintain and obtain permits for installation and operation.

How do solar power stations on the balcony work?
They usually consist of several interconnected photovoltaic panels. They are mounted on the balcony, most often on the roof, terrace, or in the garden, less frequently on the wall of the house. They are then connected to an inverter and to the electrical socket. The entire system is not difficult to install independently.
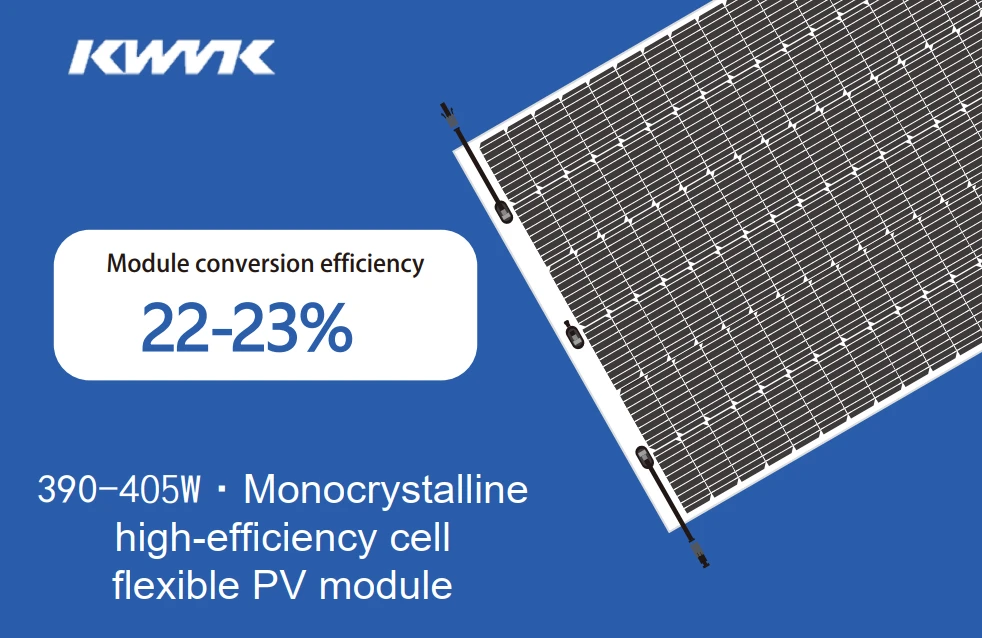
Flexible solar panels have proven themselves well on the balcony. They are characterized by an affordable price, ease of installation, and lightweight.
Sunlight, when it reaches the solar panel’s photovoltaic cells, generates electricity, resulting in an electric current. It is directed to a small “box” – an inverter, where it is converted into standard alternating current that can be used for household purposes through an electrical outlet. Most of the electricity generated in this way is used directly in the house and reduces electricity costs. Excess electricity goes into the grid.
Balcony module capacities are not high
Solar panels generate the maximum amount of electricity only under direct sunlight. Therefore, they are particularly productive in sunny areas, as well as in spring and summer. A 400-watt module can generate up to 800 kilowatt-hours of electricity per year in very sunny regions such as Africa, the Middle East, Australia, some parts of China, Latin America, and the United States. In Germany and other Central European countries, it is roughly half as much due to fewer hours of sunshine. To optimize the panels, they need to be aligned to the south at the appropriate angle. Without tilt, the output is lower: with a vertically suspended 400-watt module on a south-facing balcony in Germany, an average of around 260 kWh of electricity can be generated per year.
A properly configured 400-watt module can produce an average of around 320 kWh in spring and summer, half as much in cloudy weather, and no more than 50 kWh in heavy cloud cover. In autumn and winter, these figures are reduced by about half. The electricity generated will be sufficient to power an internet router (which consumes about 10 watts), a small refrigerator (80 watts), and a laptop (40-100 watts). For other electrical appliances, such as a computer with two monitors (up to 900 watts), a kettle (600-2000 watts), or a washing machine (about 2000 watts), additional modules will be needed.
Economic feasibility
Electricity generated by plug-in mini solar power stations is about three times cheaper. However, there are certain points to consider.
Built-in solar systems with one to three modules in German online stores cost between 400 and 1200 euros. With electricity prices ranging from 30 to 50 cents per kWh, the costs can be amortized in six to nine years. The electricity generated after this period will be free for at least another ten years. The average lifespan of modules is 25 years, and inverters last around 15 years.
At the same time, the installation of only the above-described set with one to three modules may not justify itself – the scale of generation will not be sufficient. Modern apartments consume more and more energy, especially with the growing popularity of various smart devices, “smart” bulbs and sockets, round-the-clock internet routers, and more. Compensating for these expenses with solar energy is a good idea and would be environmentally friendly. However, to fully supply an average household, ideally, the entire roof of an average-sized house would be needed.
How Safe Are Solar Systems
According to experts, plug-in solar power stations are generally very safe. However, it is recommended to purchase such devices from qualified sellers and have them installed by professional companies.
The operation of solar power stations with a maximum power of up to 600 watts on balconies is allowed in 25 out of 27 EU countries (except Belgium and Hungary). By the end of 2021, about 190,000 solar systems were installed on German balconies. China is currently the world leader in the installation of solar panels and wind turbines. In Germany, the federal government wants to significantly simplify the approval process and installation of devices connected to solar panels, and in the future, it may be possible to feed 800 watts of solar energy into the home network instead of the current 600 watts.
Choose your flexible solar panel
Source: Sobstvena Energija Doo